How to Smartly Compare Braided vs Nylon Hoses
Braided hoses offer superior durability and resistance to expansion under pressure, making them ideal for high-performance applications like brakes and hydraulics. Nylon hoses are more flexible, lighter, and often more cost-effective, suitable for general-purpose uses like fuel lines or coolant transfer where extreme pressure isn’t a primary concern. Choosing between them depends on your specific needs for pressure resistance, flexibility, and budget.
Choosing the right hose for your bike can feel like a small decision, but it makes a big difference. Are you looking for something tough enough to handle high pressure, or do you need something flexible and lightweight? Many cyclists get stuck trying to figure out whether a braided or nylon hose is the best fit for their needs. Don’t worry; it’s a common question.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to compare braided and nylon hoses. We’ll cover their strengths, weaknesses, and ideal uses. By the end, you’ll know exactly which type of hose is right for your bike. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Braided Hoses
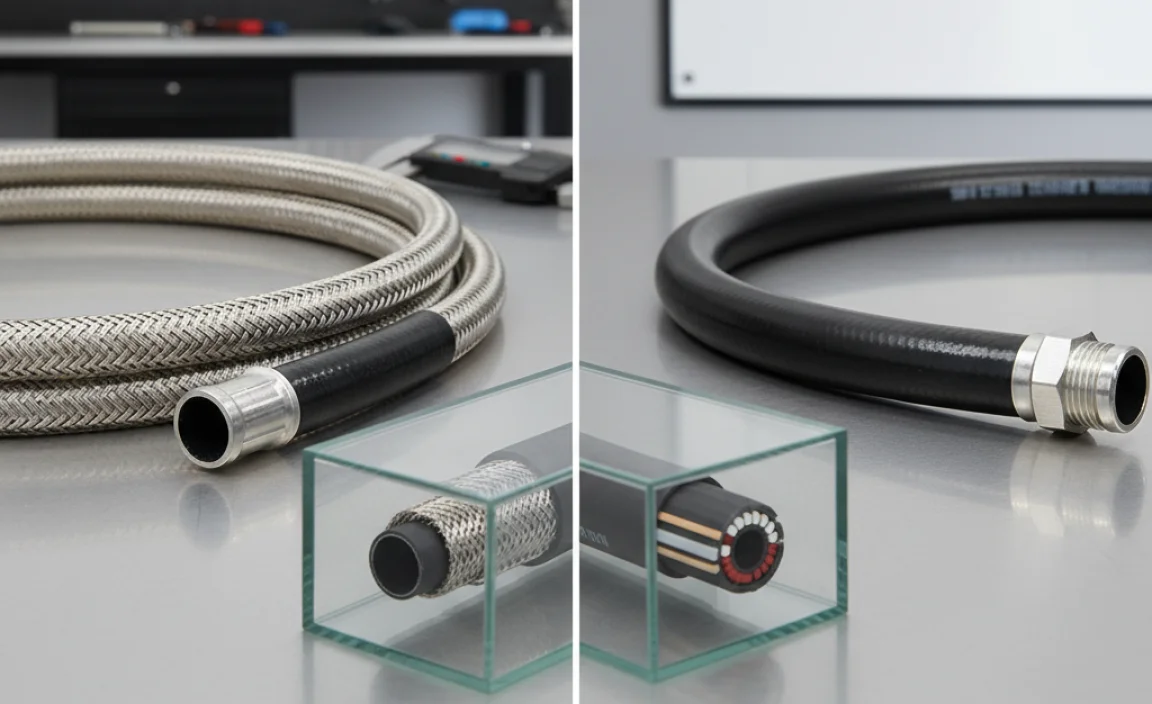

Braided hoses are known for their strength and durability. The “braiding” refers to an outer layer of woven material—typically stainless steel or another strong fiber—that reinforces the inner hose. This design gives braided hoses several key advantages.
What are Braided Hoses?
Braided hoses consist of an inner tube (often made of rubber or synthetic material) covered by a braided outer layer. This outer layer provides exceptional resistance to pressure and physical stress. The braiding prevents the hose from expanding or bursting under high pressure, making it a reliable choice for demanding applications. Learn more about hose materials and applications from resources like the Engineering ToolBox.
Advantages of Braided Hoses
- High-Pressure Resistance: Braided hoses can withstand significantly higher pressures compared to nylon hoses. This is crucial for hydraulic systems, brakes, and other high-performance applications.
- Durability: The braided outer layer protects the inner tube from abrasion, impacts, and other forms of physical damage. This extends the lifespan of the hose, even in harsh conditions.
- Minimal Expansion: The braiding prevents the hose from expanding under pressure, which ensures consistent performance and precise control in hydraulic systems.
- Temperature Resistance: Braided hoses often perform well in a wide range of temperatures, making them suitable for both hot and cold environments.
Disadvantages of Braided Hoses
- Cost: Braided hoses are generally more expensive than nylon hoses due to the materials and manufacturing processes involved.
- Weight: The added braiding layer makes these hoses heavier, which can be a concern in applications where weight is a critical factor.
- Less Flexible: Braided hoses are typically less flexible than nylon hoses, which can make them more difficult to install in tight spaces or complex routing configurations.
- Potential for Abrasion: If the outer braiding becomes damaged, it can cause abrasion to surrounding components.
Common Applications for Braided Hoses
- Hydraulic Brakes: Braided stainless steel brake lines are common in performance vehicles and bicycles for improved braking performance.
- Fuel Lines: In high-performance engines, braided fuel lines ensure a consistent fuel supply under high pressure and temperature.
- Oil Lines: Braided hoses are used to transport oil in engines and other machinery, providing durability and resistance to heat and pressure.
- Coolant Systems: In some heavy-duty applications, braided hoses are used for coolant transfer due to their temperature and pressure resistance.
Exploring Nylon Hoses

Nylon hoses offer a different set of advantages, focusing on flexibility, lightweight design, and cost-effectiveness. These hoses are made from synthetic polymers, giving them unique properties that make them suitable for various applications.
What are Nylon Hoses?
Nylon hoses are constructed from nylon or similar synthetic materials. They are known for their flexibility and resistance to chemicals and solvents. While they don’t offer the same level of pressure resistance as braided hoses, they are a practical choice for many low- to medium-pressure applications.
Advantages of Nylon Hoses
- Flexibility: Nylon hoses are highly flexible, making them easy to route through tight spaces and around obstacles.
- Lightweight: Nylon is a lightweight material, which can be an advantage in applications where minimizing weight is important.
- Cost-Effective: Nylon hoses are generally less expensive than braided hoses, making them a budget-friendly option.
- Chemical Resistance: Nylon is resistant to many chemicals and solvents, making it suitable for use with various fluids.
Disadvantages of Nylon Hoses
- Lower Pressure Resistance: Nylon hoses cannot withstand pressures as high as braided hoses.
- Temperature Limitations: Nylon may become brittle or soften at extreme temperatures, limiting its use in certain environments.
- Permeability: Nylon is more permeable than some other materials, which can lead to gradual loss of fluid or gas over time.
- Less Durable: Nylon hoses are generally less resistant to abrasion and physical damage compared to braided hoses.
Common Applications for Nylon Hoses
- Fuel Lines: In low-pressure fuel systems, nylon hoses provide a flexible and cost-effective solution.
- Coolant Transfer: Nylon hoses are often used for coolant transfer in automotive and other applications.
- Air Lines: In pneumatic systems, nylon hoses can be used for air lines and other low-pressure applications.
- Vacuum Lines: Nylon hoses are suitable for vacuum lines due to their flexibility and resistance to collapsing.
Comparing Braided vs. Nylon Hoses: A Detailed Look
To make the right choice, it’s essential to compare braided and nylon hoses across several key factors. This section provides a detailed comparison to help you understand the differences and similarities between these two types of hoses.
Pressure Resistance
Braided Hoses: Excel in high-pressure environments due to their reinforced construction. The braided outer layer prevents expansion and bursting, making them ideal for hydraulic systems and high-performance applications.
Nylon Hoses: Suited for low to medium-pressure applications. They lack the reinforcement needed to withstand high pressures, which can lead to failure or reduced performance in demanding conditions.
Flexibility
Nylon Hoses: Offer superior flexibility, making them easier to route through tight spaces and complex configurations. This flexibility simplifies installation and reduces the risk of kinking.
Braided Hoses: Less flexible due to the rigid braided layer. This can make them more challenging to install in confined areas and may require more careful planning during routing.
Durability
Braided Hoses: Highly durable, with the braided layer protecting the inner tube from abrasion, impacts, and other physical damage. This extends their lifespan, especially in harsh environments.
Nylon Hoses: Less durable and more susceptible to damage from abrasion, impacts, and exposure to harsh chemicals. They may require more frequent replacement in demanding applications.
Weight
Nylon Hoses: Lighter due to the inherent properties of nylon material. This can be an advantage in applications where minimizing weight is crucial, such as in racing vehicles or portable equipment.
Braided Hoses: Heavier because of the added braided layer. While the added weight may not be significant in all applications, it can be a factor in weight-sensitive designs.
Cost
Nylon Hoses: More cost-effective, making them a budget-friendly choice for many applications. Their lower material and manufacturing costs translate to a more affordable option.
Braided Hoses: More expensive due to the higher cost of materials and the more complex manufacturing process. The added durability and performance may justify the higher cost in critical applications.
Temperature Resistance
Braided Hoses: Generally offer better temperature resistance, performing well in a wider range of temperatures. This makes them suitable for both hot and cold environments.
Nylon Hoses: May have limitations in extreme temperatures, potentially becoming brittle in cold conditions or softening in hot conditions. This can restrict their use in certain environments.
Chemical Resistance
Nylon Hoses: Provide good resistance to many chemicals and solvents, making them suitable for use with various fluids. However, specific chemical compatibility should be verified for the intended application.
Braided Hoses: Chemical resistance depends on the material of the inner tube. Stainless steel braiding is resistant to many chemicals, but the inner tube material must also be compatible with the fluid being transported.
Lifespan
Braided Hoses: Typically have a longer lifespan due to their superior durability and resistance to physical damage. This can result in lower long-term costs, especially in demanding applications.
Nylon Hoses: May have a shorter lifespan, particularly in harsh conditions or high-pressure applications. Regular inspection and replacement may be necessary to ensure reliable performance.
Installation
Nylon Hoses: Easier to install due to their flexibility. They can be routed through tight spaces and around obstacles with less effort.
Braided Hoses: More challenging to install due to their limited flexibility. Careful planning and additional fittings may be required for complex routing configurations.
Maintenance
Braided Hoses: Require less frequent maintenance due to their durability. However, the braided layer should be inspected for damage, which could lead to abrasion of surrounding components.
Nylon Hoses: May require more frequent inspection and maintenance, especially in demanding applications. Regular checks for leaks, cracks, and other signs of wear are essential.
Key Factors to Consider Before Choosing

Before making a final decision, consider these factors to ensure you select the most appropriate hose for your needs.
Application Requirements
Identify the specific requirements of your application, including pressure, temperature, chemical exposure, and physical stress. This will help you determine which type of hose is best suited for the job. For example, high-performance braking systems require the high-pressure resistance of braided hoses.
Budget
Consider your budget and weigh the cost of each type of hose against its performance and durability. While nylon hoses are more affordable upfront, braided hoses may offer better long-term value due to their extended lifespan.
Environmental Conditions
Evaluate the environmental conditions in which the hose will be used, including temperature extremes, exposure to chemicals, and potential for physical damage. Choose a hose that can withstand these conditions without degrading or failing.
Installation Considerations
Assess the ease of installation, considering the available space and the complexity of the routing. If space is limited or the routing is complex, nylon hoses may be the better choice due to their flexibility.
Long-Term Costs
Think about the long-term costs associated with each type of hose, including maintenance, replacement, and potential downtime. While braided hoses may have a higher initial cost, their durability can result in lower long-term expenses.
Braided vs. Nylon Hoses: Side-by-Side Comparison Table

Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between braided and nylon hoses for quick reference:
| Feature | Braided Hoses | Nylon Hoses |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Resistance | High | Low to Medium |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Durability | High | Low |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Temperature Resistance | Good | Limited |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (depending on inner tube) | Good |
| Lifespan | Longer | Shorter |
| Installation | More Challenging | Easier |
| Maintenance | Less Frequent | More Frequent |
Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing the Right Hose
Follow these steps to make an informed decision when selecting between braided and nylon hoses.
- Identify the Application: Determine the specific use for the hose, such as fuel lines, brake lines, or coolant transfer.
- Assess Pressure Requirements: Determine the maximum pressure the hose will need to withstand.
- Evaluate Temperature Range: Identify the range of temperatures the hose will be exposed to.
- Consider Chemical Exposure: Determine if the hose will come into contact with any chemicals or solvents.
- Evaluate Flexibility Needs: Assess how flexible the hose needs to be for easy installation and routing.
- Set a Budget: Determine how much you are willing to spend on the hose.
- Compare Options: Use the information in this guide to compare braided and nylon hoses based on your specific needs.
- Make a Decision: Choose the hose that best meets your requirements and budget.
Tips for Maintaining Your Hoses
Proper maintenance can extend the lifespan and ensure the reliable performance of both braided and nylon hoses.
Regular Inspection
- Check for Leaks: Regularly inspect hoses for any signs of leaks, cracks, or other damage.
- Inspect Connections: Ensure that all connections are tight and secure.
- Look for Abrasion: Check for any signs of abrasion or wear, especially in areas where the hose comes into contact with other components.
Proper Installation
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Ensure that hoses are not bent sharply, as this can cause kinking and reduce their lifespan.
- Use Proper Fittings: Use the correct fittings for the type of hose and application.
- Secure Hoses: Secure hoses properly to prevent them from rubbing against other components or being exposed to excessive stress.
Cleaning and Protection
- Clean Regularly: Clean hoses regularly to remove dirt, debris, and other contaminants.
- Protect from UV Exposure: Protect hoses from prolonged exposure to sunlight, as UV radiation can degrade some materials.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Avoid exposing hoses to harsh chemicals or solvents that could damage them.
FAQ: Braided vs. Nylon Hoses
What is the main difference between braided and nylon hoses?
Braided hoses are reinforced with a braided outer layer, making them stronger and more resistant to pressure. Nylon hoses are more flexible and lightweight, suitable for lower pressure applications.
When should I use a braided hose?
Use a braided hose when you need high-pressure resistance and durability, such as in hydraulic brake systems or high-performance fuel lines.
When is a nylon hose a better choice?
Choose a nylon hose when flexibility and weight are important, and the application doesn’t require high-pressure resistance, such as in coolant transfer or low-pressure fuel systems.
Are braided hoses more durable than nylon hoses?
Yes, braided hoses are generally more durable due to their reinforced construction, which protects the inner tube from abrasion and physical damage.
Can I use a nylon hose in a high-temperature environment?
Nylon hoses may have temperature limitations, so it’s best to check the manufacturer’s specifications. Braided hoses often offer better temperature resistance.
How do I install a braided hose?
Installing a braided hose may require more careful planning due to its limited flexibility. Use proper fittings and avoid sharp bends to ensure a secure and reliable connection.
Are braided hoses worth the extra cost?
If your application requires high-pressure resistance and durability, the extra cost of a braided hose is often justified. They can provide better performance and a longer lifespan.
Conclusion
Choosing between braided and nylon hoses comes down to understanding your specific needs. Braided hoses offer superior strength and durability for high-pressure applications, while nylon hoses provide flexibility and cost-effectiveness for less demanding tasks. By considering factors like pressure resistance, flexibility, durability, and budget, you can make an informed decision that ensures optimal performance and reliability. Keep your hoses well-maintained, and they’ll keep you rolling smoothly for miles to come. Happy riding!



